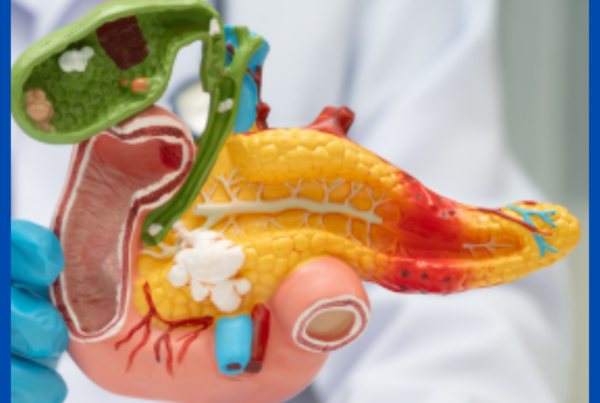
- What is the pancreas?
- The pancreas is an organ and a gland.
- The pancreas is located in the abdomen, between the spine and stomach
- It has main two functions:
- Exocrine function – Produces substance (enzymes) that
Help with digestion.
- Endocrine function – Send out hormones that control the
Amount of sugar in the bloodstream.
- What is pancreatic cancer?
- Pancreatic cancer is a disease in which malignant cancer (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the pancreas.
- Most pancreatic cancers start in the ducts of the pancreas.
- The pancreatic duct connects to the common bile duct.
- How many types of pancreatic cancer?
There are two main types of pancreatic tumors: 1. Exocrine tumors:
- 90% of all pancreatic tumors are exocrine tumors.
- The exocrine gland secretes enzymes that help break down carbohydrates, fat, proteins, and acids in the duodenum.
- Various types of exocrine pancreatic cancer like:
- Adenocarcinoma – a most common type of pancreatic cancer. This cancer occurs in the lining of the ducts in the pancreas. Adenocarcinoma develops from the cells that create pancreatic enzymes, also called acinar cell carcinoma.
- Squamous cell carcinoma – it is an extremely rare exocrine cancer. Its cell forms in the pancreatic ducts.
- Adenosquamous carcinoma – it is a rare type of pancreatic cancer that represents 1 % to 4% of exocrine pancreatic cancer.
- Colloid carcinoma – another rare type, colloid carcinoma accounts for 1% to 3% of exocrine pancreatic cancers. It is to develop from a type of benign cyst called an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
2. Neuroendocrine tumors:
- Less than 10% of pancreatic tumors are neuroendocrine tumors.
- Also known as islet cell carcinoma.
- It is developed from cells in the endocrine gland of the pancreas, which secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to regulate blood sugar.
What are the symptoms of pancreatic cancer?
- Jaundice ( yellowing skin )
- The dark color of urine
- Light-colored stool
- Upper abdominal pain
- Middle back pain
- Fatigue
- Itchy skin
- Nausea & vomiting
- Bloating
- Lack of appetite
- Blood clots
- Weight loss
- New onset diabetes
- Symptoms can vary but may include diarrhea and anemia
- Weakness
- What are causes of pancreatic cancer?
- Smoking
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Drinking a lot of alcohol
- Older age (over 65)
- Chronic inflammation of the pancreas, called pancreatitis
- Family history
- Hereditary syndromes(familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome and changes in the BRCA2 gene, lynch syndrome)
- Exposure to certain chemicals, like pesticides and petrochemicals
- How to diagnose pancreatic cancer?
- Imaging tests:
- CT scan (computes tomography)
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- PET (positron emission tomography)
- EUS (endoscopic ultrasound)
- Blood tests:
- CA 19-9
- Staging laparoscopy:
- Take a biopsy during this procedure
- Genetic testing:
- BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 (these genes as the breast cancer genes, and also indicate another type of cancer like prostate, ovarian, and pancreatic)
How is pancreatic cancer treated?
- Specific treatment depends on certain factors, including:
- Exact location of the tumor
- What stage it is
- Overall health
- Whether the cancer has spread beyond your pancreas.
Treatment:
- Surgery
- Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy)
- Distal pancreatectomy
- Total pancreatectomy
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Targeted therapy
- Pain management
How is pancreatic cancer prevented?
- Don’t smoke
- Stopped alcohol drink
- Eat lots of fresh fruit, vegetables, and whole grains
- Reduce Sugary drinks, food, and red meat
- Maintain a weight, body build
- Exercise
- Quitting tobacco usage
- Limit exposure to certain chemicals
Author :- DR. Jimmy Ladani
BHMS, CCH
Kaizen Hospital