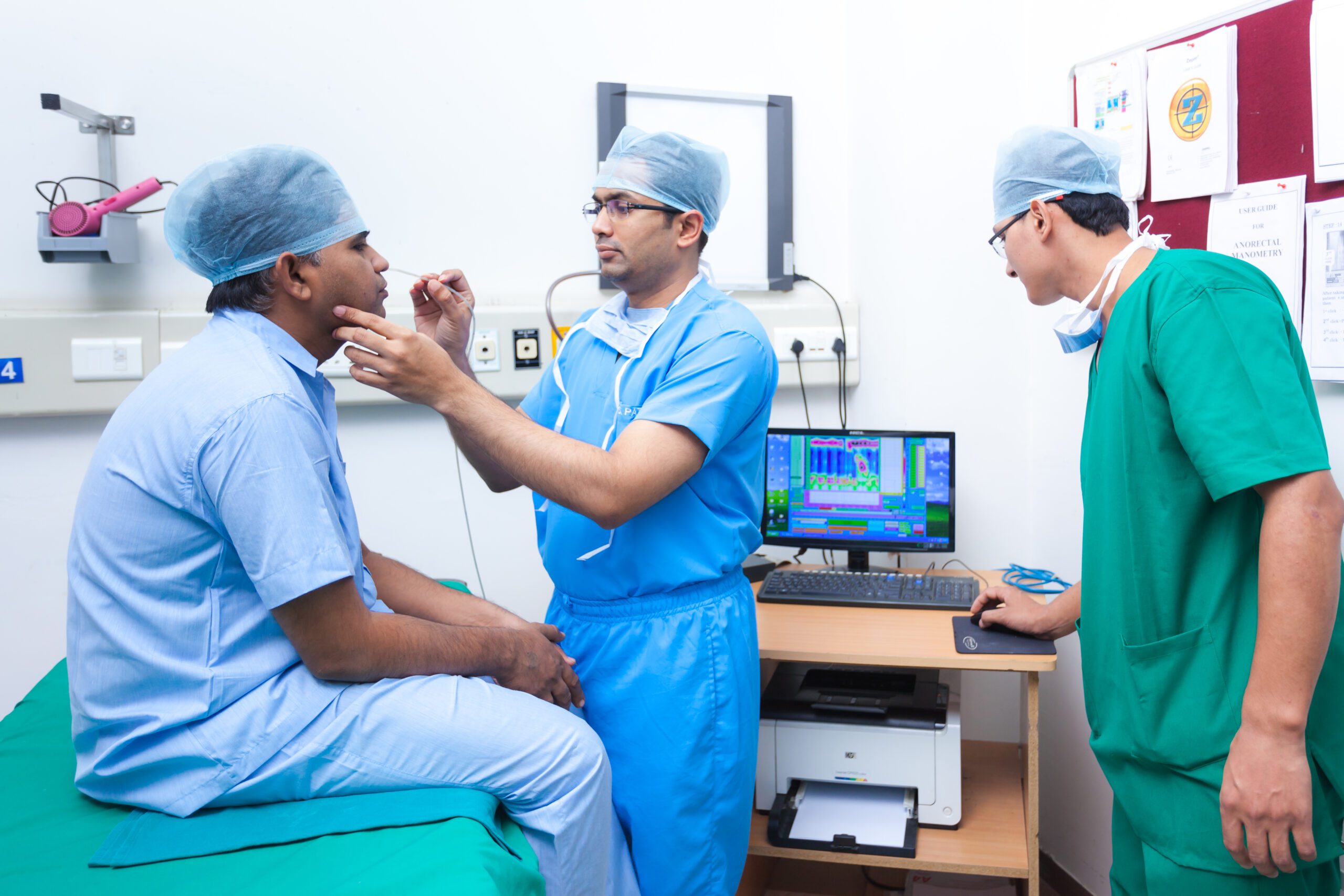
Manometry
Information about Manometry & PH Metry
What is Manometry & pH Metry?
- Esophageal Manometry is a computerised instrument to know about the smooth functioning of food pipe in our body.
- The use of 24 hours pH metry is to diagnose the disease of acid reflux
- Anorectal Manometry with biofeedback is a system which trains patient to pass stool by controlling the muscles.
When to use Esophageal Manometry & pH metry?
- Difficulty in swallowing the food(dysphagia)
- When the patient have symptoms like heaviness in chest while swallowing the food
- Burning in throat and chest (heartburn)
When to use Anorectal Manometry?
- Faecal incontinence – when patient passes stool involuntarily
- Increase frequency of stool
- Straining while passing stool
Which kind of diseases can be diagnosed?
- Achalasia Cardia
- Gerd
- Esophageal Scleroderma
- Neurogenic diseases
- Hiatus Hernia
- Esophageal Motility Disorder
- EGJ Outflow Obstruction
- Acid Reflux disease
Acid peptic disease
Peptic ulcers form when acid erodes the lining of the digestive tract. This can happen when there is excess acid in the system, or when the protective layer of mucus on the lining is broken down.
There are two major causes of peptic ulcers, bacterial infection and the use of pain relievers called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). NSAIDs include aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen.
H. pylori infection – Helicobacter pyloriis a type of bacteria that lives in the digestive tract.H. pyloriis very common; some data suggest that it is present in approximately 50 percent of people
This bacteria can cause the following, all of which can contribute to peptic ulcer formation:
- An increase in the amount of acid in the stomach and small intestine
- Inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract
- A breakdown of the protective mucous layer
NSAIDs – The use of NSAIDs can also cause peptic ulcers in some people. They are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Many people also take low-dose aspirin daily to prevent heart attack or stroke.
NSAIDs can cause changes in the protective mucous layer of the digestive tract, leading to ulcers in some people. The risk of ulcer formation depends on multiple factors, including the NSAID type, dose, and duration of use.
Other risk factors
- Genetics likely play a role,
- People who smoke cigarettes are more likely than nonsmokers to develop peptic ulcers.
- Drinking alcohol
- certain foods
- Psychological
PEPTIC ULCER SYMPTOMS
Commonest symptoms are :
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort (often a burning or hunger-like feeling)
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Stomach pain, belching, or feeling bloated after eating
- Heartburn or acid reflux
- Nausea
- Vomiting (in severe cases, there may be blood in the vomit)
- Blood in the stools (which may cause stool to appear black or tar-like)
Upper endoscopy – An upper endoscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube is inserted into the mouth and down the throat. The tube has a light and a tiny camera on the end that projects images from within the
digestive tract onto a monitor.
Ulcers can often be diagnosed through upper endoscopy. A small sample of tissue, called a biopsy, can also be taken to check for abnormal cells, cancer, or an infection withH. pylori.
Barium swallow – In some cases, a barium swallow may be done. This involves drinking a thick substance containing barium while X-rays are taken; the barium allows the digestive tract to be seen more clearly. This procedure is less common than endoscopy for diagnosing ulcers, but may be appropriate for some patients.
H. pylori testing – Anyone with a confirmed peptic ulcer should be tested forH. pyloriso that the infection, if present, can be treated.
Treatment
Treatment of Acid peptic disease includes use of drugs which decreases acid secretion, drugs which improves the mucosal barrier function and helps in healing of ulcer. Your doctor can suggest better medicine for acid peptic disease.
H Pylori infection of the stomach requires H Pylori eradication medicine which includes antibiotics as well acid suppressive medicines.
Acid Peptic Disease Treatment
H. pylori infection
This bacteria can cause the following, all of which can contribute to peptic ulcer formation:
An increase in the amount of acid in the stomach and small intestine
Inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract
A breakdown of the protective mucous layer
NSAIDs – The use of NSAIDs can also cause peptic ulcers in some people. They are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Many people also take low-dose aspirin daily to prevent heart attack or stroke.
NSAIDs can cause changes in the protective mucous layer of the digestive tract, leading to ulcers in some people. The risk of ulcer formation depends on multiple factors, including the NSAID type, dose, and duration of use.
Other risk factors
- Genetics likely play a role,
- People who smoke cigarettes are more likely than nonsmokers to develop peptic ulcers.
- Drinking alcohol
- certain foods
- Psychological
PEPTIC ULCER SYMPTOMS
Commonest symptoms are :
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort (often a burning or hunger-like feeling)
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Stomach pain, belching, or feeling bloated after eating
- Heartburn or acid reflux
- Nausea
- Vomiting (in severe cases, there may be blood in the vomit)
- Blood in the stools (which may cause stool to appear black or tar-like)
Upper endoscopy – An upper endoscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube is inserted into the mouth and down the throat. The tube has a light and a tiny camera on the end that projects images from within the
digestive tract onto a monitor.
Ulcers can often be diagnosed through upper endoscopy. A small sample of tissue, called a biopsy, can also be taken to check for abnormal cells, cancer, or an infection withH. pylori.
Barium swallow – In some cases, a barium swallow may be done. This involves drinking a thick substance containing barium while X-rays are taken; the barium allows the digestive tract to be seen more clearly. This procedure is less common than endoscopy for diagnosing ulcers, but may be appropriate for some patients.
H. pylori testing – Anyone with a confirmed peptic ulcer should be tested forH. pyloriso that the infection, if present, can be treated.
Treatment
Treatment of Acid peptic disease includes use of drugs which decreases acid secretion, drugs which improves the mucosal barrier function and helps in healing of ulcer. Your doctor can suggest better medicine for acid peptic disease.
H Pylori infection of the stomach requires H Pylori eradication medicine which includes antibiotics as well acid suppressive medicines.
H. Pylori Infection Treatment
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer is sometimes called gastric cancer. Stomach cancer is more common in men than in women and tends to occur mainly in older people. Most people who develop stomach cancer are over the age of 55.
In most cases, stomach cancer begins from a cell which is on the inside lining of the stomach (the mucosa). This type of stomach cancer is called adenocarcinoma of the stomach. As the cancer cells multiply:
Adenocarcinoma:
The tumor may invade deeper into the wall of the stomach. In time, it may pass through the wall of the stomach and invade nearby organs such as the pancreas or liver.
The tumor may spread up or down the stomach into the esophagus or small intestine.
Some cells may break off into the lymph channels or bloodstream. Cancer may then spread to nearby lymph nodes or spread to other areas of the body (metastasis).
There are some less common and rare types of stomach cancer which include:
Lymphomas: These are cancers which arise from the lymphatic tissue within the wall of the stomach.
Sarcomas: These are cancers which arise from the muscle or connective tissue within the wall of the stomach.
Carcinoid cancers: These are cancers which arise from cells in the stomach lining which make hormones.
What causes stomach cancer?
A cancerous tumor starts from one abnormal cell. The exact reason why a cell becomes cancerous is unclear. It is thought that something damages or alters certain genes in the cell. These make the cell abnormal and multiply out of control.
Many people develop stomach cancer for no apparent reason. However, certain risk factors increase the chance that stomach cancer may develop. These include:
- Ageing: Stomach cancer is more common in older people. Most cases are in people over the age of 55.
- Anemia: Having a type of anemia called pernicious anemia, which causes a lack of vitamin B12, can slightly increase your risk of stomach cancer.
- Diet is probably a factor:
- oCountries such as Japan, where people eat a lot of salt, pickled and smoked foods, have a high rate of stomach cancer.
- oEating a lot of fruit and green vegetables can reduce the risk.
- Smoking: Smokers have a higher rate of stomach cancer compared with people who do not smoke.
- H Pylori: Long-term infection of the stomach lining with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori seems to lead to a slightly higher risk of stomach cancer.
- Gender: Stomach cancer is twice as common in men as in women.
- If you have had part of your stomach removed in the past for any reason. For example, to treat a stomach ulcer or some other condition.
- Family history: For some cases, stomach cancer may run in the family. However, most cases of stomach cancer do not run in families and are not inherited.
- Blood group A: People who have this blood group have a slightly higher risk.
What are the symptoms of stomach cancer?
When a stomach cancer first develops and is small, it usually causes no symptoms. Some do not cause symptoms until they are quite advanced. Initial symptoms may include:
- Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, especially after eating.
- Indigestion.
- Feeling sick, off food. Some people have a sense of fullness after eating.
- Weight loss and/or loss of appetite.
- You may pass blood out with your faeces. You may not notice bleeding if small amounts of blood pass out with your faeces. A lot of bleeding from the stomach can turn your faeces black.
As the cancer grows in the stomach, symptoms may become worse and may include:
- The same symptoms as above, but more severe.
- Feeling generally unwell and more tired than usual.
- Becoming anemic if the tumor regularly bleeds. This can cause you to become more tired than usual.
- The cancer growing very large and causing a blockage to food and drink.
If the cancer spreads to other parts of the body, various other symptoms can develop.
How is stomach cancer diagnosed and assessed?
Initial assessment and endoscopy
If a doctor suspects that you may have stomach cancer, he or she may examine you. The examination is often normal, especially if the cancer is at an early stage. Therefore, an endoscopy is usually arranged. An endoscope is a thin, flexible, telescope. It is passed through the mouth, into the esophagus and down towards the stomach and duodenum. The endoscope contains fiber-optic channels which allow light to shine down so the doctor or nurse can see inside your stomach and duodenum.
Biopsy – to confirm the diagnosis
A biopsy is when a small sample of tissue is removed from a part of the body. The sample is then examined under the microscope to look for abnormal cells. When you have a gastroscopy, if anything abnormal is seen then the doctor or nurse can take a biopsy. This is done by passing a thin grabbing instrument down a side channel of the gastroscope. It can take two weeks for the biopsy results.
Assessing the extent and spread
If you are confirmed to have stomach cancer, further tests may be done to assess if it has spread. For example, a barium meal X-ray, a CT scan, an MRI scan, an ultrasound scans laparoscopy or other tests. This assessment is called staging of the cancer. By finding out the stage of the cancer it helps doctors to advice on the best treatment options. It also gives a reasonable indication of outlook (prognosis).
What are the treatment options for stomach cancer?
Treatment options which may be considered include surgery, chemotherapy and sometimes radiotherapy. The treatment advised for each case depends on various factors such as the stage of the cancer (how large the cancer is and whether it has spread), and your general health.
It is important to make sure you get enough nutrition from your food and you will probably be asked to see a dietician to make sure you are on the best possible diet.
Surgery
Removing the tumor may be curative if the cancer is in an early stage. The common operation is to cut out the affected part of the stomach. Sometimes the whole of the stomach is removed. Sometimes this is done laparoscopically (key-hole surgery). Even if the cancer is advanced and a cure is not possible, some surgical techniques may still have a place to ease symptoms. For example, a blockage may be eased by removing part of the stomach, or by using laser surgery or by a bypass operation.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a treatment of cancer by using anti-cancer medicines which kill cancer cells or stop them from multiplying. When chemotherapy is used in addition to surgery it is known as adjuvant chemotherapy. For example, following surgery you may be given a course of chemotherapy. This aims to kill any cancer cells which may have spread away rom the primary tumor. Sometimes, adjuvant chemotherapy is given before surgery to shrink a large tumor so that surgery is easier.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a treatment which uses high energy beams of radiation which are focused on cancerous tissue. This kills cancer cells, or stops cancer cells from multiplying. Radiotherapy is not commonly used to treat stomach cancer. It is sometimes used to reduce the size of a particular part of the cancer which is causing symptoms.
Chemoradiotherapy
In some cases a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy is offered, often as an addition to surgery. If you need to have this, it is usually done around the time of the operation.
What is the prognosis of stomach cancer?
Without treatment, a stomach cancer is likely to get larger, and spread to other parts of the body. If it is diagnosed and treated at an early stage (before growing through the wall of the stomach or spreading to lymph nodes or other areas of the body) then there is a good chance of a cure with surgery. If the cancer is diagnosed when it has grown through the wall of the stomach, or spread to other parts of the body, a cure is less likely. However, treatment can often slow down the progression of the cancer using chemotherapy medicines.
Stomach Cancer Treatment
01. HOSPITAL ADDRESS
132ft. Ring Road, Helmet Circle, Memnagar, Ahmedabad – 380052. Gujarat, India.
02. EMERGENCY( 24X7 )
Mobile: +91 – 99047 44410
Help Line : +91 – 98244 40044
+91 – 79 – 2791 4444
03. E-MAIL ADDRESS
contact@kaizenhospital.com
WHY KAIZEN ?
H. pylori infection –Helicobacter pyloriis a type of bacteria that lives in the digestive tract.H. pyloriis very common; some data suggest that it is present in approximately 50 percent of people
This bacteria can cause the following, all of which can contribute to peptic ulcer formation:
An increase in the amount of acid in the stomach and small intestine
Inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract
A breakdown of the protective mucous layer
NSAIDs – The use of NSAIDs can also cause peptic ulcers in some people. They are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Many people also take low-dose aspirin daily to prevent heart attack or stroke.
NSAIDs can cause changes in the protective mucous layer of the digestive tract, leading to ulcers in some people. The risk of ulcer formation depends on multiple factors, including the NSAID type, dose, and duration of use.
Other risk factors
- Genetics likely play a role,
- People who smoke cigarettes are more likely than nonsmokers to develop peptic ulcers.
- Drinking alcohol
- certain foods
- Psychological
PEPTIC ULCER SYMPTOMS
Commonest symptoms are :
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort (often a burning or hunger-like feeling)
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Stomach pain, belching, or feeling bloated after eating
- Heartburn or acid reflux
- Nausea
- Vomiting (in severe cases, there may be blood in the vomit)
- Blood in the stools (which may cause stool to appear black or tar-like)
Upper endoscopy – An upper endoscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube is inserted into the mouth and down the throat. The tube has a light and a tiny camera on the end that projects images from within the
digestive tract onto a monitor.
Ulcers can often be diagnosed through upper endoscopy. A small sample of tissue, called a biopsy, can also be taken to check for abnormal cells, cancer, or an infection withH. pylori.
Barium swallow – In some cases, a barium swallow may be done. This involves drinking a thick substance containing barium while X-rays are taken; the barium allows the digestive tract to be seen more clearly. This procedure is less common than endoscopy for diagnosing ulcers, but may be appropriate for some patients.
H. pylori testing – Anyone with a confirmed peptic ulcer should be tested forH. pyloriso that the infection, if present, can be treated.
Treatment
Treatment of Acid peptic disease includes use of drugs which decreases acid secretion, drugs which improves the mucosal barrier function and helps in healing of ulcer. Your doctor can suggest better medicine for acid peptic disease.
H Pylori infection of the stomach requires H Pylori eradication medicine which includes antibiotics as well acid suppressive medicines.
H. Pylori Infection Treatment

